CSS Tutorial (With Notes)
What is CSS?
- CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets
- CSS describes how HTML elements are to be displayed on screen, paper, or in other media
- CSS saves a lot of work. It can control the layout of multiple web pages all at once
- External stylesheets are stored in CSS files
CSS Demo - One HTML Page - Multiple Styles!
Here we will show one HTML page displayed with four different stylesheets. Click on the "Stylesheet 1", "Stylesheet 2", "Stylesheet 3", "Stylesheet 4" links below to see the different styles:
CSS Syntax
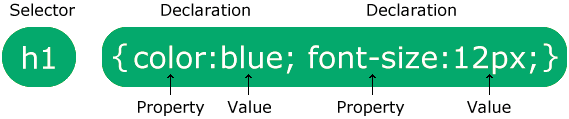
The selector points to the HTML element you want to style.
The declaration block contains one or more declarations separated by semicolons.
Each declaration includes a CSS property name and a value, separated by a colon.
Multiple CSS declarations are separated with semicolons, and declaration blocks are surrounded by curly braces
Example
In this example all <p> element will be center-aligned,with a red text color:
p{
color:red;
text-align:center;
}
Example Explained
pis a selector in CSS (it points to the HTML element you want to style: <p>).coloris a property, andredis the property valuetext-alignis a property, andcenteris the property value
CSS Selectors
CSS selectors are used to "find" (or select) the HTML elements you want to style.
We can divide CSS selectors into five categories:
- Simple selectors (select elements based on name, id, class)
- Combinator selectors (select elements based on a specific relationship between them)
- Pseudo-class selectors (select elements based on a certain state)
- Pseudo-elements selectors (select and style a part of an element)
- Attribute selectors (select elements based on an attribute or attribute value)
This page will explain the most basic CSS selectors.
The CSS element Selector
The element selector selects HTML elements based on the element name.
Example
Here, all <p> element on the page will be center-aligned,with a red text color:
p{
text-align: center;
color:red;
}
The CSS id Selector
The id selector uses the id attribute of an HTML element to select a specific element.
The id of an element is unique within a page, so the id selector is used to select one unique element!
To select an element with a specific id, write a hash (#) character, followed by the id of the element.
CSS Selectors
A CSS Selector is used to select an HTML element(s) for styling
#body is the selector
Element Selector
It is used to select an element based on the tag name
For example:
Id Selector
It is used to select an element with a given id
For example:
‘#’ is used to target by id
Example
The CSS rule below will be applied to the HTML element with id="para1":
#para1 {
text-align:center;
color: red;
}
How To Add CSS
When a browser reads a style sheet, it will format the HTML document according to the information in the style sheet
Three Ways to Insert CSS
There are three ways of inserting a style sheet:
- External CSS
- Internal CSS
- Inline CSS
External CSS
With an external style sheet, you can change the look of an entire website by changing just one file!
Each HTML page must include a reference to the external style sheet file inside the <link> element, inside the head section.
Example
External styles are defined within the <link> element,inside the <head> section of an HTML page:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<link> rel="stylesheet" href="mystyle.css">
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
An external style sheet can be written in any text editor, and must be saved with a .css extension.
The external .css file should not contain any HTML tags.
Here is how the "mystyle.css" file looks:
"mystyle.css"
body {
background-color: lightblue;
}
h1 {
color:navy;
margin-left:20px;
}
(Colors & Backgrounds)
CSS rules are simple key-value pairs with a selector. We can write CSS rules to change color and set backgrounds.
The color property
The CSS color property can be used to set the text color inside an element
Similarly, we can set color for different elements
Types of color values
Following are the most commonly used color values in CSS
- RGB: Specify color using Red, green, blue values. E.g. rgb(200,98,70)
- HEX Code: Specify color using hex code. E.g. #ff7180
- HSL: Specify the color using hsl values. E.g. hsl(8,90%,63%)
HSL stands for Hue, saturation, and lightness
The value of the color or background color is provided as any one of these values.
Note: We also have RGBA and HSLA values for color but they are rarely used by beginners. A stand for alpha
The background-color property
The CSS background-color property specifies the background color of a container.
For e.g.
The background-image property
Used to set an image as the background
The image is by default repeated in X & Y directions
The background-repeat property
Can be any of:
- repeat-x : repeat in the horizontal direction
- repeat-y : repeat in the vertical direction
- no-repeat : image not repeat
See more possible values at MDN docs
The background-size property
Can be following:
- cover : fits & no empty space remains
- contain : fits & image is fully visible
- auto : display in original size
- {{width}} : set width & height will be set automatically
- {{width}} {{height}} : set width & height
Note: Always check the MDN docs to dissect a given CSS property. Remember, practice will make you perfect
The background-position property
Sets the starting position of a background image
The background-attachment property
Defines a scrollable/non-scrollable character of a background image
The background shorthand
A single property to set multiple background properties
One of the properties can be missing given the others are in order.
- {{width}} {{height}} : set width & height
Note: Always check the MDN docs to dissect a given CSS property. Remember, practice will make you perfect
The background-position property:
Sets the starting position of a background image
The background-attachment property
Defines a scrollable/non-scrollable character of a background image.
The background shorthand
A single property to set multiple background properties
One of the properties can be missing given the others are in order.
Setting Width & Height
We can set width and height in CSS as follows
Note that the total width/height is calculated as follows:
Total height = height + top/bottom padding + top/bottom border + top/bottom margin
Setting Margin & Padding
We can set margin and padding as follows:
We can also set individual margins/padding like this:
margin-top: 70px
margin-bottom: 3px
margin-left: 8px
margin-right: 9px
#Same goes with padding also
Setting Borders
We can set the border as follows
Shorthand for above codes,
Border Radius
We can set border-radius to create rounded borders
Margin Collapse
When two margins from different elements overlap, the equivalent margin is the greater of the two. This is called margin collapse
Box Sizing
Determines what out of padding and border is included in elements width and height
Can be content-box or border-box
# Include only content in width/height
The content width and height includes, content + padding + border
(Fonts & Display)
The display property
The CSS display property is used to determine whether an element is treated as a block/inline element & the layout used for its children (flexbox/grid/etc.)
display: inline
Takes only the space required by the element. No line breaks before and after. Setting width/height (or margin/padding) not allowed.
display: block
Takes full space available in width and leaves a newline before and after the element
display: inline-block
Similar to inline but setting height, width, margin, and padding is allowed. Elements can sit next to each other
display: none vs visibility: hidden
With display: none, the element is removed from the document flow. Its space is not blocked.
With visibility: hidden, the element is hidden but its space is reserved.
text-align property
Used to set the horizontal alignment of a text
text-decoration property
Used to decorate the text
Can be overline, line-through, underline, none
text-transform property
Used to specify uppercase and lowercase letters in a text
line-height property
Used to specify the space between lines
Font
Font plays a very important role in the look and feel of a website
Font-family
Font family specifies the font of a text.
It can hold multiple values as a “fallback” system
#always follow the above technique to ensure the correct font of your choice is rendered
Web Safe Fonts
These fonts are universally installed across browsers
How to add Google Fonts
In order to use custom google fonts, go to google fonts then select a style, and finally paste it to the style.css of your page.
Other Font Properties
Some of the other font properties are listed below:
font-size: Sets the size of the font
font-style: Sets the font style
font-variant: Sets whether the text is displayed in small-caps
font-weight: sets the weight of the font
Generic Families
A broad class of similar fonts e.g. Serif, Sans-Serif
Just like when we say fruit, it can be any fruit
When we say Serif it can be any Serif font
font-family – Specific
Generic family - Generic
(Size, Position & Lists)
There are more units for describing size other than ‘px’
There are rem, em, vw, vh, percentages, etc.
What’s wrong with pixels?
Pixels (px) are relative to the viewing device.
For a device with the size 1920x1080, 1px is 1unit out of 1080/1920.
Relative lengths
These units are relative to the other length property.
Following are some of the most commonly used relative lengths,
- em – unit relative to the parent font size
em means “my parent element’s font-size”
- rem – unit relative to the root font size (<html> tag)
- vw – unit relative to 1% viewport width
- vh – unit relative to 1% viewport height
- % - unit relative to the parent element
Min/max- height/width property
CSS has a min-height, max-height, and min-width, max-width property.
If the content is smaller than the minimum height, minimum height will be applied.
Similar is the case with other related properties.
The position property
Used to manipulate the location of an element
Following are the possible values:
- static: The default position. top/bottom/left/right/z-index has no effect
- relative : The top/bottom/left/right/z-index will now work. Otherwise, the element is in the flow of the document like static.
- absolute: The element is removed from the flow and is relatively positioned to its first non-static ancestor. top/bottom etc. works
- fixed: Just like absolute except the element is positioned relative to the browser window
- sticky: The element is positioned based on the user’s scroll position
list-style property
The list-style property is a shorthand for type, position, and image
# ‘square’ in the above code is the list-style-type, ‘inside’ is the list-style-position and ‘harry.jpg’ is the list-style-image.
z-index property
The z-index property specifies the stack order of an element.
It defines which layer will be above which in case of overlapping elements
(Flexbox)
Before we look into the CSS flexbox, we will look into float and clear properties.
The float property
float property is simple. It just flows the element towards left/right
https://www.codewithharry.com/videos/css-in-one-video/#:~:text=The%20clear%20property,Initialize%20a%20flexbox*/
flex-direction property
Defines the direction towards which items are laid.
Can be row (default), row-reverse, column and column-reverse
Flex properties for parent (flex container)
Following are the properties for the flex parent:
- flex-wrap: Can be wrap, nowrap, wrap-reverse. Wrap items as needed with this property
- justify-content: Defines alignment along the main axis
- align-items: Defines alignment along the cross axis
- align-content: Aligns a flex container’s lines when there is extra space in the cross axis
Flex properties for the children (flex items)
Following are the properties for the flex children:
- order: Controls the order in which the items appear in the flex container
- align-self: Allows default alignment to be overridden for the individual flex items
- flex-grow: Defines the ability for a flex item to grow
flex-shrink: Specifies how much a flex item will shrink relative to the rest of the flex items.
(CSS Grid & Media Queries)
A CSS grid can be initialized using:
All direct children automatically become grid items
The grid-column-gap property
Used to adjust the space between the columns of a CSS grid
The grid-row-gap property
Used to adjust the space between the rows of a CSS grid
The grid-gap property
Shorthand property for grid-row-gap & grid-column-gap
Note: For a single value of grid-gap, both row and column gaps can be set in one value.
Following are the properties for grid container:
- The grid-template-columns property can be used to specify the width of columns
- The grid-template-rows property can be used to specify the height of each row
- The justify-content property is used to align the whole grid inside the container.
The align-content property is used to vertically align the whole grid inside the container.
Following are the properties for grid item:
- The grid-column property defines how many columns an items will span.
- The grid-row property defines how many rows an item will span.
- We can make an item to start on column 1 and space 3 columns like this:
CSS Media Queries
Used to apply CSS only when a certain condition is true.
Syntax:
(Transforms, Transitions & Animations)
Transforms are used to rotate, move, skew or scale elements. They are used to create a 3-D effect.
The transform property
Used to apply a 2-D or 3-D transformation to an element
The transform-origin property
Allows to change the position of transformed elements
2D transforms – can change x & y-axis
3D transforms – can change Z-axis as well
CSS 2D transform methods
You can use the following 2-D transforms in CSS:
- translate()
- rotate()
- scaleX()
- scaleY()
- skew()
- matrix()
- scale()
CSS 3D transform methods
- rotateX()
- rotateY()
- rotateZ()
CSS Transitions
Used to change property values smoothly, over a given duration
The transition property
The transition property is used to add a transition in CSS.
Following are the properties used for CSS transition:
- transition-property: The property you want to transition
- transition-duration: Time for which you want the transition to apply
- transition-timing-function: How you want the property to transition
- transition-delay: Specifies the delay for the transition
All these properties can be set using a single shorthand property
Syntax:
Transitioning multiple properties
We can transition multiple properties as follows:
CSS Animations
Used to animate CSS properties with more control.
We can use the @keyframes rule to change the animation from a given style to a new style.
Properties to add Animations
Following are the properties used to set animation in CSS:
- animation-name: name of the animation
- animation-duration: how long does the animation run?
- animation-timing-function: determines speed curve of the animation
- animation-delay: delay for the start of an animation
- animation-iteration-count: number of times an animation should run
- animation-direction: specifies the direction of the animation
Animation Shorthand
All the animation properties from 1-6 can be applied like this:
Using percentage value states with animation
We can use % values to indicate what should happen when a certain percent of animation is completed
- Can add as many intermediate properties as possible
Comments
Post a Comment